BackdoorCTF 2019
28-10-2019
Warmup (RE)
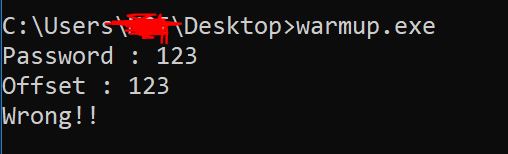
We were required to reverse a GO windows exe and provide correct value of Password and Offset to reveal the flag. Actually, the flag is the valid password.
According to the organizers, this was a warmup challenge but actually it’s not. This was a GO binary which is difficult to reverse engineer as it contains large number of functions. This exe have 2037 functions.
We have to provide two values:
-
Password: It’s the flag. A function takes this password(along with CRLF i.e. “\r\n”) as argument and returns its base64 encoded string.
-
Offset: This is an integer value which acts as seed for randomness.
rand.Intn(N)is used to generate random numbers and a function returns a random string by using those random numbers.
Pseudocode of random_string function:
str = ""
rand(seed)
for i=0; i<len(base64_of_password_plus_CRLF); i++{
randomly_generated_int = rand.Intn(25)
str += randomly_generated_int + 65
}
str is a random string
We control the seed value. So providing same seed value, each time same set of random integers will be generated.
The last check is made in encrypt_decrypt function where it XORs the random string and base64 of our password. We know the flag format is “CTF{}”. So I pass “CTF{“ as password, and any offset value. In encrypt_decrypt function, result of XOR is compared with the some hex bytes.
a = XOR( base64_of_password_plus_CRLF, random_string_of_same_size )
if(a==hex_bytes):
print("Correct!!")
else:
print("Wrong!!")
The problem is we only know first 4 bytes of flag and we also need to find the correct offset value. So reverse the XOR logic to find first few bytes of random string.
random_string = XOR(hex_bytes, base64_of_password_plus_CRLF)
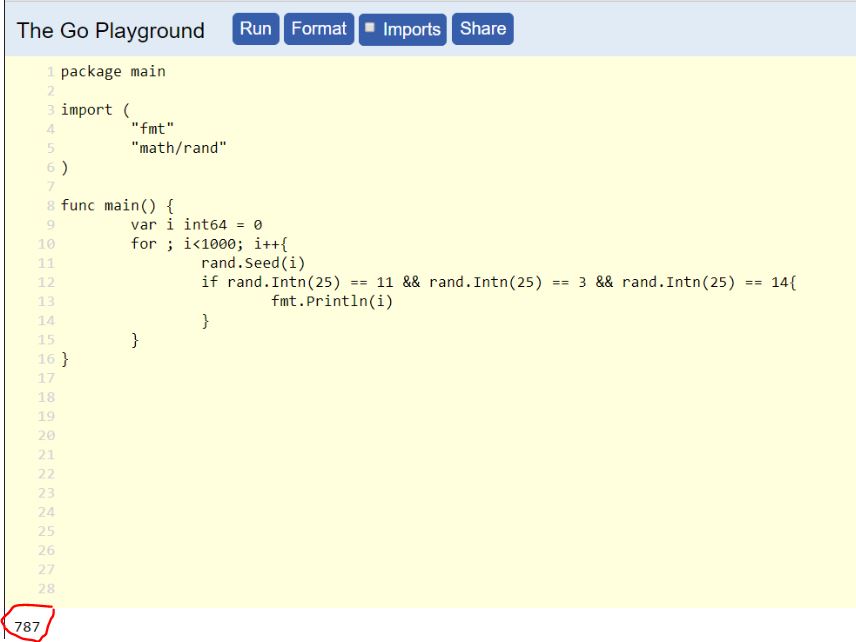
We got first few bytes of random string (“LDO..”). Now we need to find the Offset(seed) value which generates random numbers 11, 3, 14 (because ord(‘L’)-65 = 11, ord(‘D’)-65 = 3, ord(‘O’)-65 = 14). After analysing the exe in IDA, I found the seed value is less than 1000 (because seed was passed as seed = Offset % 1000).
So now we have correct seed value. Now I pass password as “A”*len_of_hex_bytes and offset value as 787 and get the random string. The following code reveals the flag:
from pwn import xor
b1 = "LDONANPIUXAKTMBP"
b2 = "YHIDLVIRHTRREMWQ"
b3 = "MLQIHJWHRGATQCHP"
a1 = "397B7C0E3E071F373E337E24091D751D".decode('hex')
a2 = "2401231F341C0C053425382F747D1F14".decode('hex')
a3 = "6D2712156D293D1F7A1E0E077B183615".decode('hex')
flag = (xor(a1[::-1], b1) + xor(a2[::-1], b2) + xor(a3[::-1], b3)).decode('base64')
print flag
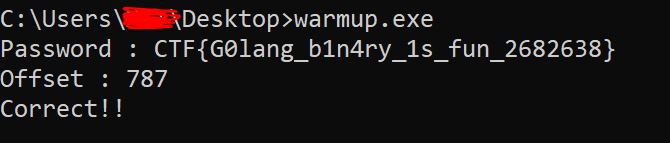
FLAG: CTF{G0lang_b1n4ry_1s_fun_2682638}